Saddam Hussein was the dictator of Iraq from 1979 until 2003. During his rule, Iraq was involved in several wars, including the Iran-Iraq War and the Gulf War. Hussein was overthrown by a U.S.-led coalition in 2003 and was later executed by the Iraqi government.
There is no evidence that Saddam Hussein was a communist. However, he did rule Iraq with an iron fist and was known for his brutal crackdowns on dissent.
There is no definitive answer to this question as it is a matter of opinion. Some people believe that Saddam Hussein was a communist, while others believe that he was not.
What political party was Saddam Hussein?
The Arab Socialist Ba’ath Party – Iraq Region was a political party founded in Iraq in 1953. The party’s goal was to unite the Arab people and create an Arab socialist state. Saddam Hussein was a leading member of the party and played a key role in the 1968 coup that brought the Ba’ath Party to power in Iraq. The Ba’ath Party espoused a mix of Arab nationalism, Iraqi nationalism and Arab socialism, and under Saddam’s leadership, Iraq became a leading Arab state.
Iraqi Neo-Ba’athism, also called Saddamism, is the ideology followed by Hussein that stipulates that Arab states should look to Iraq as the leader of the Arab “nation.” This ideology invokes militarist and nationalist rhetoric and policies.
Does Iraq have communism
The Iraqi Communist Party (ICP) is the oldest active party in Iraq, having been founded in 1934. The party has traditionally been the dominant force on the left in Iraqi politics. The ICP is a communist party, and its ideology is based on Marxism-Leninism. The party has played a significant role in the country’s history, participating in the struggle against British colonialism and later serving as a key player in the anti-Ba’athist resistance. The ICP remains an important political force in Iraq today, and continues to fight for a socialist future for the country.
The Ba’athist Iraq, also known as the Iraqi Republic, was a sovereign state that existed from 1968 to 1992. The Republic was founded on the principles of Arab nationalism and socialism, and was led by the Ba’ath Party. Saddam Hussein, the President of Iraq from 1979 to 2003, was a prominent member of the Ba’ath Party and played a significant role in the Republic’s government.
Was Saddam a Soviet ally?
Iraq has been a close ally of the Soviets since 1958, and in 1972, the two countries signed a Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation. Under this treaty, both countries promised to help each other under threat and to avoid entering hostile alliances against one another. However, relations between the two countries have deteriorated in recent years, and Iraq has been moving closer to the US and other Western countries.
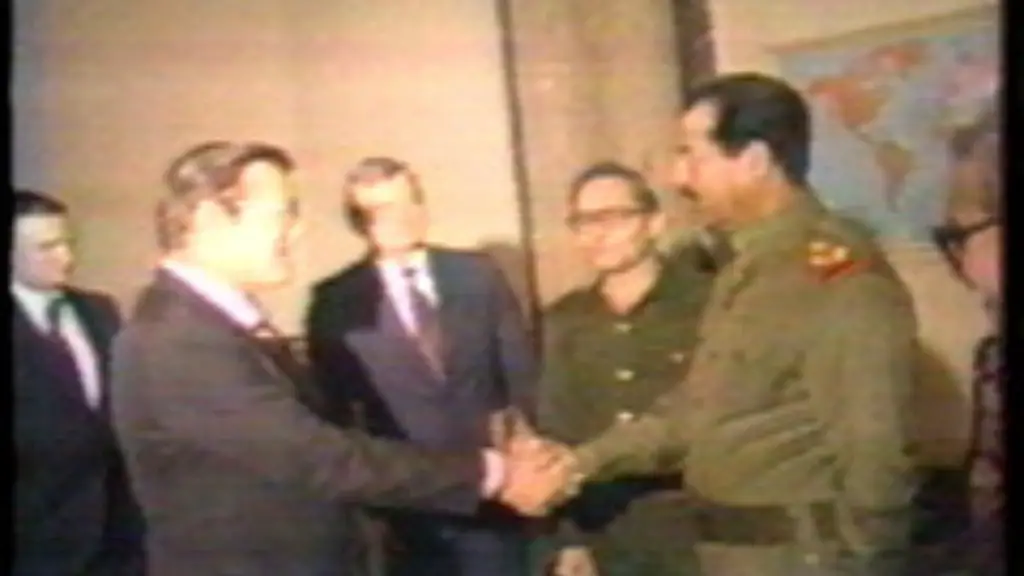
The US provided significant intelligence support to Saddam Hussein’s military during the Iran-Iraq war. This included combat planning assistance and battlefield intelligence such as satellite pictures. However, the US did not provide direct military support to Iraq during the war.
What did Saddam Hussein do that was good?
Hussein has been denounced in the past by some for modernizing Iraq, using its oil wealth to improve conditions for the general population.
It is clear that Mohisan has great respect for Saddam Hussein. He believes that Saddam was an honest person who cared for his people. He also admires Saddam’s strength and believes that he was a great leader.
Was Iraq better under Saddam
Iraq was definitely safer and wealthier before any American intervention. Saddam was a cruel dictator, but he kept Iraq fairly stable and safe from outside threats. It was only when the Americans came in and toppled his regime that Iraq became a lawless, chaotic place. The Americans then imposed harsh sanctions on the country, which made life extremely difficult for ordinary Iraqis. It’s no wonder that they have grown sick of their way of life and want to see a change.
The United States and Iraq have a strong bilateral relationship that is based on the US-Iraq Strategic Framework Agreement (SFA). The SFA provides the framework for US engagement with Iraq on diplomatic, political, economic, and security issues. The United States is committed to supporting Iraq in its efforts to build a stable, prosperous, and democratic country.
Is Iraq still a free country?
Iraq is a federal parliamentary republic and the president is the head of state. The prime minister is the head of government, and the constitution provides for two deliberative bodies, the Council of Representatives and the Council of Union. The judiciary is free and independent of the executive and the legislature.
The Constitution of Iraq establishes the Iraqi government as a federal parliamentary representative democratic republic. This type of government is characterized by a Constitution that divides powers between a central government and devolved regional governments. The central government is responsible for defense, foreign affairs, and national security, while the devolved governments manage internal affairs. This system ensures that the Iraqi people are represented at both the national and local levels.
Why did the US want to stop Saddam Hussein
The Iraq War was justified by the US government on the grounds of disarming Iraq of weapons of mass destruction, ending Saddam Hussein’s support for terrorism, and freeing the Iraqi people. However, many critics argue that these rationalizations were simply pretexts for launching a war of aggression.
Saddam Husayn’s decision to invade Iran in 1980 is generally ascribed to two main motives. One is that he invaded for geopolitical gain when international factors worked in his favor. The other is that he invaded to prevent Iran from fomenting revolution in Iraq.
The first motive is supported by the fact that, at the time of the invasion, Saddam Husayn was in a strong position internationally. The Iranian Revolution of 1979 had deposed the Shah of Iran, a key ally of the United States, and replaced him with the Islamic Republic of Iran, a regime hostile to both the U.S. and Saddam Husayn’s regime in Iraq. This created an opportunity for Saddam Husayn to improve Iraq’s relations with the U.S. by aligning himself with the latter’s enemy.
The second motive is supported by the fact that, at the time of the invasion, Iran was in the midst of a revolution that had the potential to spread to Iraq. Saddam Husayn saw the Iranian Revolution as a threat to his own regime, and so he sought to quash it by invading Iran.
What was Saddam Hussein’s religion?
Saddam adhered to an eccentric interpretation of Islam that Ba’thist intellectuals had developed in the mid-twentieth century. For him and many other Ba’thists, Islam was the religion of the Arabs Muhammad was an Arab prophet who preached a divine message intended for his Arab followers.
Saddam Hussein was the fifth President of Iraq, serving in this role from 1979 until 2003. He was born in Tikrit, Iraq, and his native language is Arabic. Saddam was deposed following the 2003 invasion of Iraq and was later executed by the Iraqi government in 2006.
Which countries supported Saddam
Hussein’s relations with the Soviet Union were good, and he received advanced weapons systems from them. He also developed a tenuous relationship with the United States, who supported him during the Iran-Iraq War.
Iran and Iraq are indeed close allies, and this is largely due to the fact that both countries share a Shi’ite system of governance. The two countries have been supporting each other against the Islamic State, and this has resulted in a strong relationship between them.
Final Words
Saddam Hussein was not a communist.
There is no concrete evidence that Saddam Hussein was a communist, but there are some indications that he may have supported communist ideals. For example, he nationalized Iraq’s oil industry and developed close ties with the Soviet Union. However, Saddam Hussein was ultimately a Ba’athist, and not a communist.